- 1. Getting Started
-
2.
First Semester Topics
-
General Chemistry Review
- Introduction
- Electron Configurations of Atoms
- QM Description of Orbitals
- Practice Time - Electron Configurations
- Hybridization
- Strategy to Determine Hybridization
- Practice Time! - Hybridization
- Formal Charge
- Practice Time - Formal Charge
- Acids-bases
- Practice Time - Acids and Bases
- Hydrogen Bonding is a Verb!
- Progress Pulse
-
Structure and Bonding
- Chemical Intuition
- From Quantum Mechanics to the Blackboard: The Power of Approximations
- Atomic Orbitals
- Electron Configurations of Atoms
- Electron Configurations Tutorial
- Practice Time - Structure and Bonding 1
- Lewis Structures
- Drawing Lewis Structures
- Valence Bond Theory
- Valence Bond Theory Tutorial
- Hybridization
- Polar Covalent Bonds
- Formal Charge
- Practice Time - Structure and Bonding 2
- Curved Arrow Notation
- Resonance
- Electrons behave like waves
- MO Theory Intro
- Structural Representations
- Progress Pulse
-
Acids/Base and Reactions
- Reactions
- Reaction Arrows: What do they mean?
- Thermodynamics of Reactions
- Acids Intro
- Practice Time! Generating a conjugate base.
- Lewis Acids and Bases
- pKa Scale
- Practice Time! pKa's
- Predicting Acid-Base Reactions from pKa
- Structure and Acidity
- Structure and Acidity II
- Practice Time! Structure and Acidity
- Curved Arrows and Reactions
- Nucleophiles
- Electrophiles
- Practice Time! Identifying Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
- Mechanisms and Arrow Pushing
- Practice Time! Mechanisms and Reactions
- Energy Diagrams and Reactions
- Practice Time! - Energy Diagrams
- Progress Pulse
- Introduction to Retrosynthesis
-
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
- Introduction to Hydrocarbons and Alkanes
- Occurrence
- Functional Groups
- Practice Time! Functional Groups.
- Structure of Alkanes - Structure of Methane
- Structure of Alkanes - Structure of Ethane
- Naming Alkanes
- Practice Time! Naming Alkanes
- Relative Stability of Acyclic Alkanes
- Physical Properties of Alkanes
- Ranking Boiling Point and Solubility of Compounds
- Conformations of Acyclic Alkanes
- Practice Time! Conformations of acyclic alkanes.
- Conformations of Cyclic Alkanes
- Naming Bicyclic Compounds
- Stability of Cycloalkane (Combustion Analysis)
- Degree of Unsaturation
-
Stereochemistry
- Enalapril in ACE
- Constitutional and Stereoisomers
- Chirality or Handedness
- Drawing a Molecules Mirror Image
- Exploring Mirror Image Structures
- Enantiomers
- Drawing Enantiomers
- Practice Time! Drawing Enantiomers
- Identifying Chiral Centers
- Practice Time! Identifying Chiral Molecules
- CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) Priorities
- Determining R/S Configuration
- Diastereomers
- Meso Compounds
- Fischer Projections
- Fischer Projections: Carbohydrates
- Measuring Chiral Purity
- Practice Time! - Determining Chiral Purity and ee
- Chirality and Drugs
- Chiral Synthesis
- Prochirality
- Converting Fischer Projections to Zig-zag Structures
- Practice Time! - Assigning R/S Configurations
-
Alkenes and Addition Reactions
- The Structure of Alkenes
- Alkene Structure - Ethene
- Naming Alkenes
- Health Insight - BVO (Brominated Vegetable Oil)
- E/Z and CIP
- Stability of Alkenes
- H-X Addition to Alkenes: Hydrohalogenation
- Practice Time - Hydrohalogenation
- X2 Addition to Alkenes: Halogenation
- HOX addition: Halohydrins
- Practice Time - Halogenation
- Hydroboration/Oxidation of Alkenes: Hydration
- Practice Time - Hydroboration-Oxidation
- Oxymercuration-Reduction: Hydration
- Practice Time - Oxymercuration/Reduction
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
- Calculating Oxidation States of Carbon
- Identifying oxidation and reduction reactions
- Practice Time - Oxidation and Reduction in Organic
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Capsaicin
- Alkynes
- Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
- Substitutions (SN1/SN2) and Eliminations (E1/E2)
- Dienes, Allylic and Benzylic systems
-
General Chemistry Review
-
3.
Second Semester Topics
- Arenes and Aromaticity
-
Reactions of Arenes
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- EAS-Halogenation
- EAS-Nitration
- Practice Time - Synthesis of Aniline
- EAS-Alkylation
- Practice Time - Friedel Crafts Alkylation
- EAS-Acylation
- Practice Time - Synthesis of Alkyl Arenes
- EAS-Sulfonation
- Practice Time - EAS
- Effect on Rate and Orientation
- Donation and Withdrawal of Electrons
- Regiochemistry in EAS
- Practice Time - Directing Group Effects
- Steric Considerations
- Synthesizing Poly-substituted Benzene's
- NAS - Addition/Elimination
- NAS - Elimination/Addition - Benzyne
- Alcohols and Phenols
-
Ethers and Epoxides
- Intro and Occurrence
- Crown Ethers and Cryptands
- Preparation of Ethers
- Reactions of Ethers
- Practice Time - Ethers
- Preparation of Epoxides
- Reactions of Epoxides - Acidic Ring Opening
- Practice Time - Acidic Ring Opening
- Reactions of Epoxides - Nucleophilic Ring Opening
- Practice Time - Nucleophilic Ring opening
- Application - Epoxidation in Reboxetine Synthesis
- Application - Nucleophilic Epoxide Ring Opening in Crixivan Synthesis
- Naming Ethers and Epoxides
-
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Naming Aldehydes and Ketones
- Practice Time - Naming Aldehydes/Ketones
- Nucleophilic addition
- Addition of Water - Gem Diols
- Practice Time - Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Addition of Alcohols - Hemiacetals and Acetals
- Acetal Protecting Groups
- Hemiacetals in Carbohydrates
- Practice Time - Hemiacetals and Acetals
- Addition of Amines - Imines
- Addition of Amines - Enamines
- Practice Time - Imines and Enamines
- Application - Imatinab Enamine Synthesis
- Addition of CN - Cyanohydrins
- Practice Time - Cyanohydrins
- Application - Isentress Synthesis
- Addition of Ylides - Wittig Reaction
- Practice Time - Wittig Olefination
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
- Enols and Enolates
- Condensation Reactions
- 4. Spectroscopy - NMR, IR and UV
-
5.
General Chemistry
- General Chemistry Lab
- Calculator Tips for Chemistry
- Significant Figures
- Practice Time! Significant Figures
- Spreadsheets - Getting Started
- Spreadsheets - Charts and Trend lines
- Standard Deviation
- Standard Deviation Calculations
- Factor Labels
- Practice Time! - Factor Labels
- Limiting Reagent Problem
- Percent Composition
- Molar Mass Calculation
- Average Atomic Mass
- Empirical Formula
- Practice time! Empirical and Molecular Formulae
- Initial Rate Analysis
- Practice Time! Initial Rate Analysis
- Solving Equilibrium Problems with ICE
- Practice Time! Equilibrium ICE Tables
- Le Chatelier's
- Practice Time! Le Chatelier's Principle
- 6. Organic Chemistry Lab
-
7.
Question Of The Day
- 8. Tools and Reference
-
9.
Tutorials
- Reaction Mechanisms (introduction)
- Factor Labels
- Acetylides and Synthesis
- Drawing Cyclohexane Chair Structures
- Drawing Lewis Structures
- Aromaticity Tutorial
- Common Named Aromatics (Crossword Puzzle)
- Functional Groups (Flashcards)
- Characteristic Reactions of Functional Groups
- Alkyl and Alkenyl Groups
- Valence Bond Theory
- Alkane Nomenclature
Clear History
Quick Menu
Mechanisms
SN1 Substitution Nucleophilic - Unimolecular
The SN1 mechanism involves two steps:
-
Formation of the Carbocation (Rate-Determining Step):
- The leaving group (LG) dissociates from the substrate, forming a positively charged carbocation intermediate.
- The rate of the reaction depends only on the concentration of the substrate ([R-LG]), not the nucleophile, as the nucleophile is not involved in the rate-determining step.
- Rate = k[R-LG]
- Carbocation stability plays a crucial role: tertiary (3°) > secondary (2°) > primary (1°) > methyl, due to increasing carbocation stability through inductive effects and hyperconjugation.
For example, if you placed tert-butyl chloride in water it would undergo the following substitution, replacing the Cl atom with water.
- Nucleophilic Attack on the Carbocation:
-
- The nucleophile rapidly attacks the planar carbocation to form the final substituted product.
- Since the carbocation is planar, the nucleophile can attack from either side, leading to no stereochemical preference and often resulting in a racemic mixture if the starting material is chiral.
A water molecule will eventually attach the cation to form an alkoxonium, which is subsequently deprotonated to form the corresponding alcohol.
-
Key Characteristics of SN1 Mechanism:
- Nucleophile: The strength of the nucleophile is not crucial since it does not influence the rate of the reaction.
- Stereochemistry: The intermediate carbocation is planar, leading to loss of stereochemical information. If the starting material is chiral, the product will typically be a racemic mixture.
- Solvent: SN1 reactions are favored in polar solvents, especially polar protic solvents like water or alcohols. These solvents stabilize the carbocation intermediate and solvate the leaving group, making its dissociation easier.
SN2 Substitution Nucleophilic - Bimolecular
The SN2 mechanism is a single-step, concerted reaction that follows the rate law:
-
Single-Step Mechanism (Bimolecular Nucleophilic Substitution):
- The nucleophile directly attacks the substrate from the opposite side (Back side attack) of the leaving group. This backside attack leads to the simultaneous breaking of the bond to the leaving group and the formation of the bond to the nucleophile.
- Since this is a concerted process, the reaction proceeds in a single step without forming intermediates.
- Rate = k[R-LG][Nu⁻]
- The rate depends on both the concentration of the substrate ([R-LG]) and the nucleophile ([Nu⁻]).
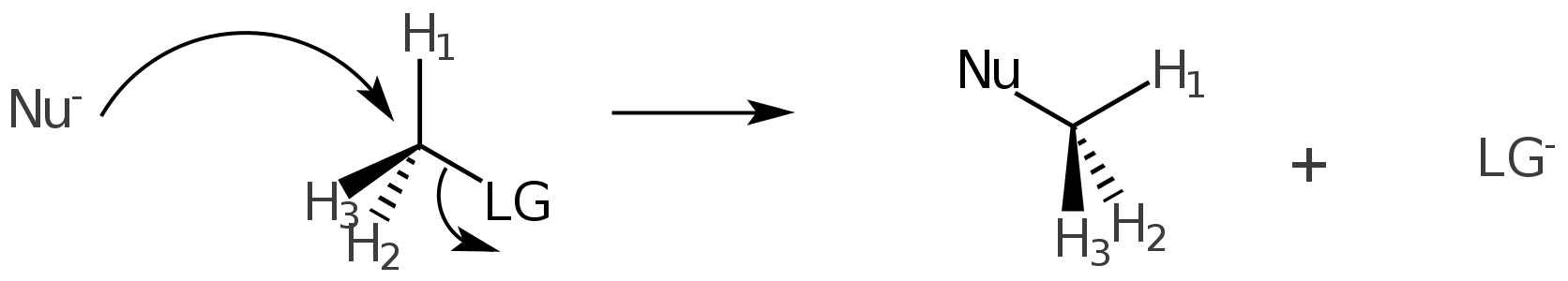
Key Characteristics of SN2 Mechanism:
-
Nucleophile:
- A strong nucleophile is required to attack the substrate effectively, as it directly affects the reaction rate.
- Nucleophiles with a negative charge or lone pairs (e.g., OH⁻, CN⁻, or I⁻) are typically more effective.
- Nucleophile sterics are important.
-
Solvent:
- SN2 reactions are favored in polar aprotic solvents (e.g., DMSO, acetone, DMF). These solvents stabilize the nucleophile less, allowing it to remain highly reactive.
-
Stereochemistry:
- The reaction results in complete inversion of configuration (Walden Inversion) at the reactive carbon center, making it stereospecific.
-
Substrate:
- Sterically accessible substrates (e.g., methyl or primary carbons) react faster. Secondary carbons are slower, and tertiary carbons are essentially unreactive in SN2 due to steric hindrance.
-
Rate Law:
Rate = k[R-LG][Nu⁻]
The reaction rate depends on both the nucleophile and the substrate, making it bimolecular.
Why backside attack?
- LG is in the way for frontside attack
- Backside has the required empty antibonding orbital to accept electrons from Nu (Nucleophile)
