- 1. Getting Started
-
2.
First Semester Topics
-
General Chemistry Review
- Introduction
- Electron Configurations of Atoms
- QM Description of Orbitals
- Practice Time - Electron Configurations
- Hybridization
- Closer Look at Hybridization
- Strategy to Determine Hybridization
- Practice Time! - Hybridization
- Formal Charge
- Practice Time - Formal Charge
- Acids-bases
- Practice Time - Acids and Bases
- Hydrogen Bonding is a Verb!
- Progress Pulse
-
Structure and Bonding
- Chemical Intuition
- From Quantum Mechanics to the Blackboard: The Power of Approximations
- Atomic Orbitals
- Electron Configurations of Atoms
- Electron Configurations Tutorial
- Practice Time - Structure and Bonding 1
- Lewis Structures
- Drawing Lewis Structures
- Valence Bond Theory
- Valence Bond Theory Tutorial
- Hybridization
- Polar Covalent Bonds
- Formal Charge
- Practice Time - Structure and Bonding 2
- Curved Arrow Notation
- Resonance
- Electrons behave like waves
- MO Theory Intro
- Structural Representations
- Progress Pulse
-
Acids/Base and Reactions
- Reactions
- Reaction Arrows: What do they mean?
- Thermodynamics of Reactions
- Acids Intro
- Practice Time! Generating a conjugate base.
- Lewis Acids and Bases
- pKa Scale
- Practice Time! pKa's
- Predicting Acid-Base Reactions from pKa
- Structure and Acidity
- Structure and Acidity II
- Practice Time! Structure and Acidity
- Curved Arrows and Reactions
- Nucleophiles
- Electrophiles
- Practice Time! Identifying Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
- Mechanisms and Arrow Pushing
- Practice Time! Mechanisms and Reactions
- Energy Diagrams and Reactions
- Practice Time! - Energy Diagrams
- Progress Pulse
- Introduction to Retrosynthesis
-
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
- Introduction to Hydrocarbons and Alkanes
- Occurrence
- Functional Groups
- Practice Time! Functional Groups.
- Structure of Alkanes - Structure of Methane
- Structure of Alkanes - Structure of Ethane
- Naming Alkanes
- Practice Time! Naming Alkanes
- Alkane Isomers
- Relative Stability of Acyclic Alkanes
- Physical Properties of Alkanes
- Ranking Boiling Point and Solubility of Compounds
- Conformations of Acyclic Alkanes
- Practice Time! Conformations of acyclic alkanes.
- Conformations of Cyclic Alkanes
- Naming Bicyclic Compounds
- Stability of Cycloalkane (Combustion Analysis)
- Degree of Unsaturation
-
Stereochemistry
- Enalapril in ACE
- Constitutional and Stereoisomers
- Chirality or Handedness
- Drawing a Molecules Mirror Image
- Exploring Mirror Image Structures
- Enantiomers
- Drawing Enantiomers
- Practice Time! Drawing Enantiomers
- Identifying Chiral Centers
- Practice Time! Identifying Chiral Molecules
- CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) Priorities
- Determining R/S Configuration
- Diastereomers
- Meso Compounds
- Fischer Projections
- Fischer Projections: Carbohydrates
- Measuring Chiral Purity
- Practice Time! - Determining Chiral Purity and ee
- Chirality and Drugs
- Chiral Synthesis
- Prochirality
- Converting Fischer Projections to Zig-zag Structures
- Practice Time! - Assigning R/S Configurations
-
Alkenes and Addition Reactions
- The Structure of Alkenes
- Alkene Structure - Ethene
- Physical Properties of Alkenes
- Naming Alkenes
- Health Insight - BVO (Brominated Vegetable Oil)
- E/Z and CIP
- Stability of Alkenes
- H-X Addition to Alkenes: Hydrohalogenation
- Practice Time - Hydrohalogenation
- X2 Addition to Alkenes: Halogenation
- HOX addition: Halohydrins
- Practice Time - Halogenation
- Hydroboration/Oxidation of Alkenes: Hydration
- Practice Time - Hydroboration-Oxidation
- Oxymercuration-Reduction: Hydration
- Practice Time - Oxymercuration/Reduction
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
- Calculating Oxidation States of Carbon
- Identifying oxidation and reduction reactions
- Practice Time - Oxidation and Reduction in Organic
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Capsaicin
-
Alkynes
- Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene)
- Naming Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Naming Alkynes
- Physical Properties of Alkynes
- Preparation of Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Preparation of Alkynes
- H-X Addition to Alkynes
- X2 Addition
- Hydration
- Reduction of Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Addition Reactions of Alkynes
- Oxidative Cleavage of Alkynes
- Alkyne Acidity and Acetylide Anions
- Reactions of Acetylide Anions
- Retrosynthesis Revisted
- Practice Time! - Multistep Synthesis Using Acetylides
-
Alkyl Halides and Alcohol
- Naming Alkyl Halides
- Naming Alcohols
- Classes of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
- Practice Time! - Naming Alkyl Halides
- Practice Time! - Naming Alcohols
- Physical Properties of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
- Structure and Reactivity of Alcohols
- Structure and Reactivity of Alkyl Halides
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides and Tosylates from Alcohols
- Practice Time! - Alcohols to Alkyl Halides
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alkenes; Allylic Bromination
- Strategy for Predicting Products of Allylic Brominations
- Practice Time! - Allylic Bromination
- Substitutions (SN1/SN2) and Eliminations (E1/E2)
- Dienes, Allylic and Benzylic systems
-
General Chemistry Review
-
3.
Second Semester Topics
- Arenes and Aromaticity
-
Reactions of Arenes
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- EAS-Halogenation
- EAS-Nitration
- Practice Time - Synthesis of Aniline
- EAS-Alkylation
- Practice Time - Friedel Crafts Alkylation
- EAS-Acylation
- Practice Time - Synthesis of Alkyl Arenes
- EAS-Sulfonation
- Practice Time - EAS
- Donation and Withdrawal of Electrons
- Regiochemistry in EAS
- Practice Time - Directing Group Effects
- Synthesizing Disubstituted Benzenes: Effects of Substituents on Rate and Orientation
- Steric Considerations
- Strategies for Synthesizing Disubstituted Benzenes
- NAS - Addition/Elimination
- NAS - Elimination/Addition - Benzyne
- Alcohols and Phenols
-
Ethers and Epoxides
- Intro and Occurrence
- Crown Ethers and Cryptands
- Preparation of Ethers
- Reactions of Ethers
- Practice Time - Ethers
- Preparation of Epoxides
- Reactions of Epoxides - Acidic Ring Opening
- Practice Time - Acidic Ring Opening
- Reactions of Epoxides - Nucleophilic Ring Opening
- Practice Time - Nucleophilic Ring opening
- Application - Epoxidation in Reboxetine Synthesis
- Application - Nucleophilic Epoxide Ring Opening in Crixivan Synthesis
- Physical Properties of Ethers and Epoxides
- Naming Ethers and Epoxides
-
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Naming Aldehydes and Ketones
- Physical Properties of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Practice Time - Naming Aldehydes/Ketones
- Nucleophilic addition
- Addition of Water - Gem Diols
- Practice Time - Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Addition of Alcohols - Hemiacetals and Acetals
- Acetal Protecting Groups
- Hemiacetals in Carbohydrates
- Practice Time - Hemiacetals and Acetals
- Addition of Amines - Imines
- Addition of Amines - Enamines
- Practice Time - Imines and Enamines
- Application - Imatinab Enamine Synthesis
- Addition of CN - Cyanohydrins
- Practice Time - Cyanohydrins
- Application - Isentress Synthesis
- Addition of Ylides - Wittig Reaction
- Practice Time - Wittig Olefination
- Structure of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
- Enols and Enolates
- Condensation Reactions
- 4. Spectroscopy - NMR, IR and UV
-
5.
General Chemistry
- General Chemistry Lab
- Strategy for Balancing Chemical Reactions
- Calculator Tips for Chemistry
- Significant Figures
- Practice Time! Significant Figures
- Spreadsheets - Getting Started
- Spreadsheets - Charts and Trend lines
- Standard Deviation
- Standard Deviation Calculations
- Factor Labels
- Practice Time! - Factor Labels
- Limiting Reagent Problem
- Percent Composition
- Molar Mass Calculation
- Average Atomic Mass
- Empirical Formula
- Practice time! Empirical and Molecular Formulae
- Initial Rate Analysis
- Practice Time! Initial Rate Analysis
- Solving Equilibrium Problems with ICE
- Practice Time! Equilibrium ICE Tables
- Le Chatelier's
- Practice Time! Le Chatelier's Principle
- 6. Organic Chemistry Lab
-
7.
Question Of The Day
- 8. Tools and Reference
-
9.
Tutorials
- Reaction Mechanisms (introduction)
- Factor Labels
- Acetylides and Synthesis
- Drawing Cyclohexane Chair Structures
- Drawing Lewis Structures
- Aromaticity Tutorial
- Common Named Aromatics (Crossword Puzzle)
- Functional Groups (Flashcards)
- Characteristic Reactions of Functional Groups
- Alkyl and Alkenyl Groups
- Valence Bond Theory
- Alkane Nomenclature
Clear History
Intro to UV Spectroscopy
In UV spectroscopy molecules or materials are irradiated with ultraviolet radiation. The UV radiation is absorbed by the molecules and in doing so an electron is bumped (excited) from a low lying HOMO to a higher energy LUMO.
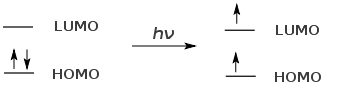
Ground State Excited State (Higher E)
The difference in energy between the excited and ground state is referred to as the HOMO-LUMO gap. The HOMO-LUMO gap is effected by the functional groups attached to the double bond and to the degree of conjugation.
In general
- The more conjugation the lower the HOMO-LUMO gap (larger λmax).
- The more alkyl substituents the lower the HOMO-LUMO gap (larger λmax).
Interpreting UV spectra
A UV spectra has absorbance on the y-axis and wavelength of UV radiation on the x-axis. Recall that the amount of light absorbed by a collection of molecule is governed by Beer's law. There is normally a maximum in wavelength observed in a UV spectra which is designated λmax. For example below is the UV spectra for Lycopene and its λmax=471 nm (nanometers).
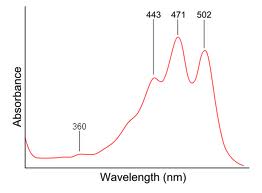
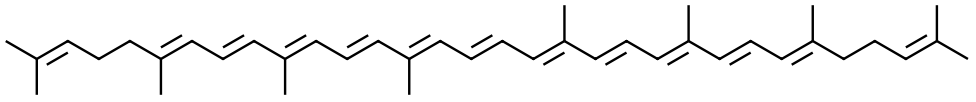
Lycopene is highly conjugated having 11 double bonds in conjugation and therefore has a small HOMO-LUMO gap. In general the smaller the HOMO-LUMO gap energy, the lower the energy of the photon absorbed. Recall that the energy of a photon E = hν = hc/λ. So the smaller the HOMO-LUMO gap the larger the λmax.
Lycopene's λmax=471, which is in the blue end of the spectrum. Since Lycopene absorbs all the blue light, all other light namely the red light is reflected and as a result appears red in ripe tomatoes.
Lycopene
Below are the wavelengths of visible light. Notice how the λmax=471 is in the blue region.
| Color | wavelength (nm) |
| Red | 630-700 |
| Orange | 590-630 |
| Yellow | 560-590 |
| Green | 450-490 |
| Blue | 450-490 |
| Indigo | 420-440 |
| Violet | 400-450 |
Structure and λmax
As discussed above the;
- The more conjugation the lower the HOMO-LUMO gap (larger λmax).
- The more alkyl substituents the lower the HOMO-LUMO gap (larger λmax).
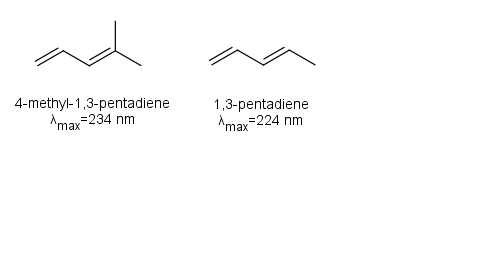
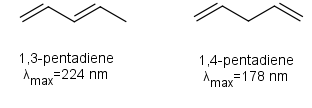
Thus 1,3-pentadiene would have a smaller HOMO-LUMO gap and therefore a larger λmax than 1,4-pentadiene. Note that 1,3-pentadiene is conjugated, while 1,4-pentadiene is not conjugated.
Adding an alkyl group such as a methyl group increases the λmax. For example 4-methyl-1,3-pentadiene has a greater λmax than 1,3-pentadiene.