- 1. Getting Started
-
2.
First Semester Topics
-
General Chemistry Review
- Introduction
- Electron Configurations of Atoms
- QM Description of Orbitals
- Practice Time - Electron Configurations
- Hybridization
- Closer Look at Hybridization
- Strategy to Determine Hybridization
- Practice Time! - Hybridization
- Formal Charge
- Practice Time - Formal Charge
- Acids-bases
- Practice Time - Acids and Bases
- Hydrogen Bonding is a Verb!
- Progress Pulse
-
Structure and Bonding
- Chemical Intuition
- From Quantum Mechanics to the Blackboard: The Power of Approximations
- Atomic Orbitals
- Electron Configurations of Atoms
- Electron Configurations Tutorial
- Practice Time - Structure and Bonding 1
- Lewis Structures
- Drawing Lewis Structures
- Valence Bond Theory
- Valence Bond Theory Tutorial
- Hybridization
- Polar Covalent Bonds
- Formal Charge
- Practice Time - Structure and Bonding 2
- Curved Arrow Notation
- Resonance
- Electrons behave like waves
- MO Theory Intro
- Structural Representations
- Progress Pulse
-
Acids/Base and Reactions
- Reactions
- Reaction Arrows: What do they mean?
- Thermodynamics of Reactions
- Acids Intro
- Practice Time! Generating a conjugate base.
- Lewis Acids and Bases
- pKa Scale
- Practice Time! pKa's
- Predicting Acid-Base Reactions from pKa
- Structure and Acidity
- Structure and Acidity II
- Practice Time! Structure and Acidity
- Curved Arrows and Reactions
- Nucleophiles
- Electrophiles
- Practice Time! Identifying Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
- Mechanisms and Arrow Pushing
- Practice Time! Mechanisms and Reactions
- Energy Diagrams and Reactions
- Practice Time! - Energy Diagrams
- Progress Pulse
- Introduction to Retrosynthesis
-
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
- Introduction to Hydrocarbons and Alkanes
- Occurrence
- Functional Groups
- Practice Time! Functional Groups.
- Structure of Alkanes - Structure of Methane
- Structure of Alkanes - Structure of Ethane
- Naming Alkanes
- Practice Time! Naming Alkanes
- Alkane Isomers
- Relative Stability of Acyclic Alkanes
- Physical Properties of Alkanes
- Ranking Boiling Point and Solubility of Compounds
- Conformations of Acyclic Alkanes
- Practice Time! Conformations of acyclic alkanes.
- Conformations of Cyclic Alkanes
- Naming Bicyclic Compounds
- Stability of Cycloalkane (Combustion Analysis)
- Degree of Unsaturation
-
Stereochemistry
- Enalapril in ACE
- Constitutional and Stereoisomers
- Chirality or Handedness
- Drawing a Molecules Mirror Image
- Exploring Mirror Image Structures
- Enantiomers
- Drawing Enantiomers
- Practice Time! Drawing Enantiomers
- Identifying Chiral Centers
- Practice Time! Identifying Chiral Molecules
- CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) Priorities
- Determining R/S Configuration
- Diastereomers
- Meso Compounds
- Fischer Projections
- Fischer Projections: Carbohydrates
- Measuring Chiral Purity
- Practice Time! - Determining Chiral Purity and ee
- Chirality and Drugs
- Chiral Synthesis
- Prochirality
- Converting Fischer Projections to Zig-zag Structures
- Practice Time! - Assigning R/S Configurations
-
Alkenes and Addition Reactions
- The Structure of Alkenes
- Alkene Structure - Ethene
- Physical Properties of Alkenes
- Naming Alkenes
- Health Insight - BVO (Brominated Vegetable Oil)
- E/Z and CIP
- Stability of Alkenes
- H-X Addition to Alkenes: Hydrohalogenation
- Practice Time - Hydrohalogenation
- X2 Addition to Alkenes: Halogenation
- HOX addition: Halohydrins
- Practice Time - Halogenation
- Hydroboration/Oxidation of Alkenes: Hydration
- Practice Time - Hydroboration-Oxidation
- Oxymercuration-Reduction: Hydration
- Practice Time - Oxymercuration/Reduction
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
- Calculating Oxidation States of Carbon
- Identifying oxidation and reduction reactions
- Practice Time - Oxidation and Reduction in Organic
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Capsaicin
-
Alkynes
- Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene)
- Naming Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Naming Alkynes
- Physical Properties of Alkynes
- Preparation of Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Preparation of Alkynes
- H-X Addition to Alkynes
- X2 Addition
- Hydration
- Reduction of Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Addition Reactions of Alkynes
- Oxidative Cleavage of Alkynes
- Alkyne Acidity and Acetylide Anions
- Reactions of Acetylide Anions
- Retrosynthesis Revisted
- Practice Time! - Multistep Synthesis Using Acetylides
-
Alkyl Halides and Alcohol
- Naming Alkyl Halides
- Naming Alcohols
- Classes of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
- Practice Time! - Naming Alkyl Halides
- Practice Time! - Naming Alcohols
- Physical Properties of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
- Structure and Reactivity of Alcohols
- Structure and Reactivity of Alkyl Halides
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides and Tosylates from Alcohols
- Practice Time! - Alcohols to Alkyl Halides
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alkenes; Allylic Bromination
- Strategy for Predicting Products of Allylic Brominations
- Practice Time! - Allylic Bromination
-
Substitutions (SN1/SN2) and Eliminations (E1/E2)
- Introduction
- Solvents
- SN1 Reaction: The Carbocation Pathway
- SN2 Reactions: The Concerted Backside Attack
- SN1 vs. SN2: Choosing the Right Path
- Application: Cardura (Doxazosin)
- E1 Reactions: Elimination via Carbocations
- E2 Reactions: The Concerted Elimination
- E1cB: The Conjugate Base Elimination Pathway
- Substitution versus Elimination
- Dienes, Allylic and Benzylic systems
-
General Chemistry Review
-
3.
Second Semester Topics
- Arenes and Aromaticity
-
Reactions of Arenes
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- EAS-Halogenation
- EAS-Nitration
- Practice Time - Synthesis of Aniline
- EAS-Alkylation
- Practice Time - Friedel Crafts Alkylation
- EAS-Acylation
- Practice Time - Synthesis of Alkyl Arenes
- EAS-Sulfonation
- Practice Time - EAS
- Donation and Withdrawal of Electrons
- Regiochemistry in EAS
- Practice Time - Directing Group Effects
- Synthesizing Disubstituted Benzenes: Effects of Substituents on Rate and Orientation
- Steric Considerations
- Strategies for Synthesizing Disubstituted Benzenes
- NAS - Addition/Elimination
- NAS - Elimination/Addition - Benzyne
- Alcohols and Phenols
-
Ethers and Epoxides
- Intro and Occurrence
- Crown Ethers and Cryptands
- Preparation of Ethers
- Reactions of Ethers
- Practice Time - Ethers
- Preparation of Epoxides
- Reactions of Epoxides - Acidic Ring Opening
- Practice Time - Acidic Ring Opening
- Reactions of Epoxides - Nucleophilic Ring Opening
- Practice Time - Nucleophilic Ring opening
- Application - Epoxidation in Reboxetine Synthesis
- Application - Nucleophilic Epoxide Ring Opening in Crixivan Synthesis
- Physical Properties of Ethers and Epoxides
- Naming Ethers and Epoxides
-
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Naming Aldehydes and Ketones
- Physical Properties of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Practice Time - Naming Aldehydes/Ketones
- Nucleophilic addition
- Addition of Water - Gem Diols
- Practice Time - Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Addition of Alcohols - Hemiacetals and Acetals
- Acetal Protecting Groups
- Hemiacetals in Carbohydrates
- Practice Time - Hemiacetals and Acetals
- Addition of Amines - Imines
- Addition of Amines - Enamines
- Practice Time - Imines and Enamines
- Application - Imatinab Enamine Synthesis
- Addition of CN - Cyanohydrins
- Practice Time - Cyanohydrins
- Application - Isentress Synthesis
- Addition of Ylides - Wittig Reaction
- Practice Time - Wittig Olefination
- Structure of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
- Enols and Enolates
- Condensation Reactions
-
4.
NMR, IR, UV and MS
- Spectroscopy
-
HNMR
- Nuclear Spin
- Interpreting
- Chemical Shift
- Practice Time! - Chemical Shift
- Equivalency
- Indentifying Homotopic, Enantiotopic and Diastereotopic Protons
- Practice Time! - Equivalency
- Intensity of Signals
- Spin Spin Splitting
- Practice Time! - Spin-Spin Splitting
- Primer on ¹³C NMR Spectroscopy
- Alkanes
- Alkynes
- Alcohols
- Alkenes
- Coupling in Cis/Trans Alkenes
- Ketones
- HNMR Practice 1
- HNMR Practice 2
- HNMR Practice 3
- HNMR Practice 4
- Exchangeable Protons and Deuterium Exchange
- IR - Infrared Spectroscopy
- UV - Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
- Mass Spectrometry
-
5.
General Chemistry
- General Chemistry Lab
- Strategy for Balancing Chemical Reactions
- Calculator Tips for Chemistry
- Significant Figures
- Practice Time! Significant Figures
- Spreadsheets - Getting Started
- Spreadsheets - Charts and Trend lines
- Standard Deviation
- Standard Deviation Calculations
- Factor Labels
- Practice Time! - Factor Labels
- Limiting Reagent Problem
- Percent Composition
- Molar Mass Calculation
- Average Atomic Mass
- Empirical Formula
- Practice time! Empirical and Molecular Formulae
- Initial Rate Analysis
- Practice Time! Initial Rate Analysis
- Solving Equilibrium Problems with ICE
- Practice Time! Equilibrium ICE Tables
- Le Chatelier's
- Practice Time! Le Chatelier's Principle
- 6. Organic Chemistry Lab
- 7. Tools and Reference
-
8.
Tutorials
- Reaction Mechanisms (introduction)
- Factor Labels
- Acetylides and Synthesis
- Drawing Cyclohexane Chair Structures
- Drawing Lewis Structures
- Aromaticity Tutorial
- Common Named Aromatics (Crossword Puzzle)
- Functional Groups (Flashcards)
- Characteristic Reactions of Functional Groups
- Alkyl and Alkenyl Groups
- Valence Bond Theory
- Alkane Nomenclature
-
9.
The Alchemy of Drug Development
- Ivermectin: From Merck Innovation to Global Health Impact
- The Fen-Phen Fix: A Weight Loss Dream Turned Heartbreak
- The Asymmetry of Harm: Thalidomide and the Power of Molecular Shape
- Semaglutide (Ozempic): From Lizard Spit to a Once-Weekly Wonder
- From Cocaine to Novocain: The Development of Safer Local Anesthesia
- The Crixivan Saga: A Targeted Strike Against HIV
- The story of Merck’s COX-2 inhibitor, Vioxx (rofecoxib)
- The Accidental Aphrodisiac: The Story of Viagra
- THC: A Double-Edged Sword with Potential Neuroprotective Properties?
- Ritonavir Near Disaster and Polymorphism
- 10. Allied Health Chem
Clear History
18 Electron Practice Problems
Practice Problems: 18-Electron Rule
Question 1: Hexacarbonyl Manganese ([Mn(CO)₆]⁺)
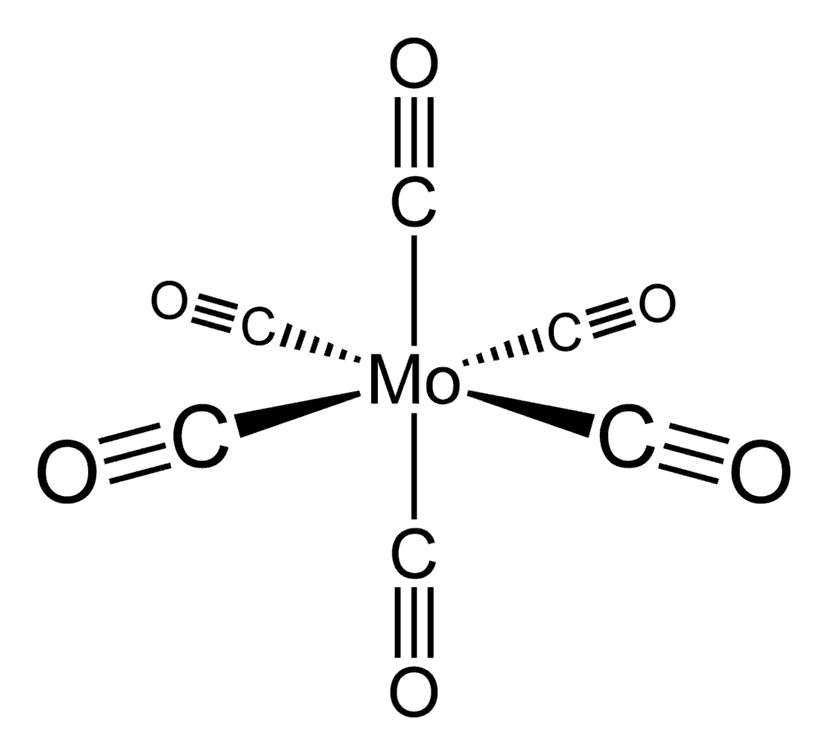
Determine the electron count for the complex [Mn(CO)₆]⁺. Does it satisfy the 18-electron rule?
Answer:
- Metal and oxidation state:
- Manganese (Mn) is in Group 7. The +1 charge means Mn is in the +1 oxidation state.
- Mn contributes 6 electrons (7 − 1 = 6). (d6 metal)
- Ligand contributions:
- Each CO ligand contributes 2 electrons. With 6 CO ligands: 6 × 2 = 12 electrons.
- Total electron count:
- 6 (Mn) + 12 (CO ligands) = 18 electrons.
- Conclusion:
- [Mn(CO)₆]⁺ satisfies the 18-electron rule and is stable.
Question 2: Tetrachloronickelate ([NiCl₄]²⁻)
2NiCl4.svg.png)
Determine the electron count for [NiCl₄]²⁻. Does it satisfy the 18-electron rule?
Answer:
- Metal and oxidation state:
- Nickel (Ni) is in Group 10. The 2⁻ charge means Ni is in the +2 oxidation state.
- Ni contributes 8 electrons (10 − 2 = 8). (therefore d8 metal)
- Ligand contributions:
- Each Cl⁻ ligand contributes 2 electrons. With 4 Cl⁻ ligands: 4 × 2 = 8 electrons.
- Total electron count:
- 8 (Ni) + 8 (Cl⁻ ligands) = 16 electrons.
- Conclusion:
- [NiCl₄]²⁻ does not satisfy the 18-electron rule but is stable as a 16-electron tetrahedral complex.
Question 3: Bis(benzene)chromium ([Cr(η⁶-C₆H₆)₂])
chromium-2D-skeletal.png)
Determine the electron count for [Cr(η⁶-C₆H₆)₂]. Does it satisfy the 18-electron rule?
Answer:
- Metal and oxidation state:
- Chromium (Cr) is in Group 6 and is in the 0 oxidation state.
- Cr contributes 6 electrons. (d6 metal)
- Ligand contributions:
- Each η⁶-C₆H₆ (benzene) ligand contributes 6 electrons. With 2 benzene ligands: 2 × 6 = 12 electrons.
- Total electron count:
- 6 (Cr) + 12 (benzene ligands) = 18 electrons.
- Conclusion:
- [Cr(η⁶-C₆H₆)₂] satisfies the 18-electron rule and is stable.
Question 4: Tricarbonyl Iron Hydride ([HFe(CO)₃])
Determine the electron count for [HFe(CO)₃]. Does it satisfy the 18-electron rule?
Answer:
- Metal and oxidation state:
- Iron (Fe) is in Group 8 and is in the +1 oxidation state (H⁻ is treated as a ligand, making Fe effectively +1).
- Fe contributes 7 electrons (8 − 1 = 7) so its a d7 metal.
- Ligand contributions:
- Each CO ligand contributes 2 electrons. With 3 CO ligands: 3 × 2 = 6 electrons.
- The H⁻ ligand contributes 2 electrons.
- Total electron count:
- 7 (Fe) + 6 (CO ligands) + 2 (H⁻) = 15 electrons.
- Conclusion:
- [HFe(CO)₃] does not satisfy the 18-electron rule and is a 15-electron complex, which is less stable and reactive.
Question 5: Rhodium Carbonyl Chloride ([RhCl(CO)(PPh₃)₂])
Determine the electron count for [RhCl(CO)(PPh₃)₂]. Does it satisfy the 18-electron rule?
Answer:
- Metal and oxidation state:
- Rhodium (Rh) is in Group 9 and is in the +1 oxidation state.
- Rh contributes 8 electrons (9 − 1 = 8).
- Ligand contributions:
- The CO ligand contributes 2 electrons.
- The Cl⁻ ligand contributes 2 electrons.
- Each PPh₃ ligand contributes 2 electrons. With 2 PPh₃ ligands: 2 × 2 = 4 electrons.
- Total electron count:
- 8 (Rh) + 2 (CO) + 2 (Cl⁻) + 4 (PPh₃ ligands) = 16 electrons.
- Conclusion:
- [RhCl(CO)(PPh₃)₂] is a stable 16-electron complex due to steric and electronic factors.
Question 6: Hexacarbonyl Chromium ([Cr(CO)₆])
Determine the electron count for [Cr(CO)₆]. Does it satisfy the 18-electron rule?
Answer:
- Metal and oxidation state:
- Chromium (Cr) is in Group 6 and is in the 0 oxidation state.
- Cr contributes 6 electrons.
- Ligand contributions:
- Each CO ligand contributes 2 electrons. With 6 CO ligands: 6 × 2 = 12 electrons.
- Total electron count:
- 6 (Cr) + 12 (CO ligands) = 18 electrons.
- Conclusion:
- [Cr(CO)₆] satisfies the 18-electron rule and is stable.
Question 7: Tetracarbonyl Nickel ([Ni(CO)₄])
Determine the electron count for [Ni(CO)₄]. Does it satisfy the 18-electron rule?
Answer:
- Metal and oxidation state:
- Nickel (Ni) is in Group 10 and is in the 0 oxidation state.
- Ni contributes 10 electrons.
- Ligand contributions:
- Each CO ligand contributes 2 electrons. With 4 CO ligands: 4 × 2 = 8 electrons.
- Total electron count:
- 10 (Ni) + 8 (CO ligands) = 18 electrons.
- Conclusion:
- [Ni(CO)₄] satisfies the 18-electron rule and is stable.
Question 8: Determine Oxidation State of the Metal
Question: The complex [Mo(CO)₄(PPh₃)₂] is known to have a total of 18 electrons. Using this information, determine the oxidation state of molybdenum in this complex.
Answer:
-
Ligand contributions:
-
Each CO contributes 2 electrons: 4 × 2 = 8 electrons.
-
Each PPh₃ contributes 2 electrons: 2 × 2 = 4 electrons.
-
Total from ligands: 8 + 4 = 12 electrons.
-
-
Metal contribution:
-
For the complex to have 18 electrons, the metal must contribute: 18 − 12 = 6 electrons.
-
-
Determine the oxidation state:
-
Molybdenum (Mo) is in Group 6, so a neutral Mo atom contributes 6 electrons.
-
Since Mo contributes all 6 electrons, it must be in the 0 oxidation state.
-
-
Conclusion:
-
Molybdenum is in the 0 oxidation state in [Mo(CO)₄(PPh₃)₂].
-
Question 9: Determine Oxidation State of the Metal
Question: The complex [FeCp(CO)₂]⁺ has a total of 18 electrons. What is the oxidation state of iron in this complex?
Answer:
-
Ligand contributions:
-
The Cp ligand contributes 6 electrons.
-
Each CO ligand contributes 2 electrons: 2 × 2 = 4 electrons.
-
Total from ligands: 6 + 4 = 10 electrons.
-
-
Metal contribution:
-
For the complex to have 18 electrons, the metal must contribute: 18 − 10 = 8 electrons.
-
-
Determine the oxidation state:
-
Iron (Fe) is in Group 8, so a neutral Fe atom contributes 8 electrons.
-
Since Fe contributes all 8 electrons, it is in the 0 oxidation state.
-
-
Conclusion:
-
Iron is in the 0 oxidation state in [FeCp(CO)₂]⁺.
-
Question 10: Determine Oxidation State of the Metal
Question: The complex [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺ is a 16-electron species. What is the oxidation state of cobalt in this complex?
Answer:
-
Ligand contributions:
-
Each NH₃ contributes 2 electrons: 6 × 2 = 12 electrons.
-
-
Metal contribution:
-
For the complex to have 16 electrons, the metal must contribute: 16 − 12 = 4 electrons.
-
-
Determine the oxidation state:
-
Cobalt (Co) is in Group 9, so a neutral Co atom contributes 9 electrons.
-
To contribute only 4 electrons, cobalt must lose 5 electrons.
-
Oxidation state = +5.
-
-
Conclusion:
-
Cobalt is in the +5 oxidation state in [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺.
-