- 1. Getting Started
-
2.
First Semester Topics
-
General Chemistry Review
- Introduction
- Electron Configurations of Atoms
- QM Description of Orbitals
- Practice Time - Electron Configurations
- Hybridization
- Closer Look at Hybridization
- Strategy to Determine Hybridization
- Practice Time! - Hybridization
- Formal Charge
- Practice Time - Formal Charge
- Acids-bases
- Practice Time - Acids and Bases
- Hydrogen Bonding is a Verb!
- Progress Pulse
-
Structure and Bonding
- Chemical Intuition
- From Quantum Mechanics to the Blackboard: The Power of Approximations
- Atomic Orbitals
- Electron Configurations of Atoms
- Electron Configurations Tutorial
- Practice Time - Structure and Bonding 1
- Lewis Structures
- Drawing Lewis Structures
- Valence Bond Theory
- Valence Bond Theory Tutorial
- Hybridization
- Polar Covalent Bonds
- Formal Charge
- Practice Time - Structure and Bonding 2
- Curved Arrow Notation
- Resonance
- Electrons behave like waves
- MO Theory Intro
- Structural Representations
- Progress Pulse
-
Acids/Base and Reactions
- Reactions
- Reaction Arrows: What do they mean?
- Thermodynamics of Reactions
- Acids Intro
- Practice Time! Generating a conjugate base.
- Lewis Acids and Bases
- pKa Scale
- Practice Time! pKa's
- Predicting Acid-Base Reactions from pKa
- Structure and Acidity
- Structure and Acidity II
- Practice Time! Structure and Acidity
- Curved Arrows and Reactions
- Nucleophiles
- Electrophiles
- Practice Time! Identifying Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
- Mechanisms and Arrow Pushing
- Practice Time! Mechanisms and Reactions
- Energy Diagrams and Reactions
- Practice Time! - Energy Diagrams
- Progress Pulse
- Introduction to Retrosynthesis
-
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
- Introduction to Hydrocarbons and Alkanes
- Occurrence
- Functional Groups
- Practice Time! Functional Groups.
- Structure of Alkanes - Structure of Methane
- Structure of Alkanes - Structure of Ethane
- Naming Alkanes
- Practice Time! Naming Alkanes
- Alkane Isomers
- Relative Stability of Acyclic Alkanes
- Physical Properties of Alkanes
- Ranking Boiling Point and Solubility of Compounds
- Conformations of Acyclic Alkanes
- Practice Time! Conformations of acyclic alkanes.
- Conformations of Cyclic Alkanes
- Naming Bicyclic Compounds
- Stability of Cycloalkane (Combustion Analysis)
- Degree of Unsaturation
-
Stereochemistry
- Enalapril in ACE
- Constitutional and Stereoisomers
- Chirality or Handedness
- Drawing a Molecules Mirror Image
- Exploring Mirror Image Structures
- Enantiomers
- Drawing Enantiomers
- Practice Time! Drawing Enantiomers
- Identifying Chiral Centers
- Practice Time! Identifying Chiral Molecules
- CIP (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog) Priorities
- Determining R/S Configuration
- Diastereomers
- Meso Compounds
- Fischer Projections
- Fischer Projections: Carbohydrates
- Measuring Chiral Purity
- Practice Time! - Determining Chiral Purity and ee
- Chirality and Drugs
- Chiral Synthesis
- Prochirality
- Converting Fischer Projections to Zig-zag Structures
- Practice Time! - Assigning R/S Configurations
-
Alkenes and Addition Reactions
- The Structure of Alkenes
- Alkene Structure - Ethene
- Physical Properties of Alkenes
- Naming Alkenes
- Health Insight - BVO (Brominated Vegetable Oil)
- E/Z and CIP
- Stability of Alkenes
- H-X Addition to Alkenes: Hydrohalogenation
- Practice Time - Hydrohalogenation
- X2 Addition to Alkenes: Halogenation
- HOX addition: Halohydrins
- Practice Time - Halogenation
- Hydroboration/Oxidation of Alkenes: Hydration
- Practice Time - Hydroboration-Oxidation
- Oxymercuration-Reduction: Hydration
- Practice Time - Oxymercuration/Reduction
- Oxidation and Reduction in Organic Chemistry
- Calculating Oxidation States of Carbon
- Identifying oxidation and reduction reactions
- Practice Time - Oxidation and Reduction in Organic
- Oxidation
- Reduction
- Capsaicin
-
Alkynes
- Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene)
- Naming Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Naming Alkynes
- Physical Properties of Alkynes
- Preparation of Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Preparation of Alkynes
- H-X Addition to Alkynes
- X2 Addition
- Hydration
- Reduction of Alkynes
- Practice Time! - Addition Reactions of Alkynes
- Oxidative Cleavage of Alkynes
- Alkyne Acidity and Acetylide Anions
- Reactions of Acetylide Anions
- Retrosynthesis Revisted
- Practice Time! - Multistep Synthesis Using Acetylides
-
Alkyl Halides and Alcohol
- Naming Alkyl Halides
- Naming Alcohols
- Classes of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
- Practice Time! - Naming Alkyl Halides
- Practice Time! - Naming Alcohols
- Physical Properties of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
- Structure and Reactivity of Alcohols
- Structure and Reactivity of Alkyl Halides
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides and Tosylates from Alcohols
- Practice Time! - Alcohols to Alkyl Halides
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alkenes; Allylic Bromination
- Strategy for Predicting Products of Allylic Brominations
- Practice Time! - Allylic Bromination
-
Substitutions (SN1/SN2) and Eliminations (E1/E2)
- Introduction
- Solvents
- SN1 Reaction: The Carbocation Pathway
- SN2 Reactions: The Concerted Backside Attack
- SN1 vs. SN2: Choosing the Right Path
- Application: Cardura (Doxazosin)
- E1 Reactions: Elimination via Carbocations
- E2 Reactions: The Concerted Elimination
- E1cB: The Conjugate Base Elimination Pathway
- Substitution versus Elimination
- Dienes, Allylic and Benzylic systems
-
General Chemistry Review
-
3.
Second Semester Topics
- Arenes and Aromaticity
-
Reactions of Arenes
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
- EAS-Halogenation
- EAS-Nitration
- Practice Time - Synthesis of Aniline
- EAS-Alkylation
- Practice Time - Friedel Crafts Alkylation
- EAS-Acylation
- Practice Time - Synthesis of Alkyl Arenes
- EAS-Sulfonation
- Practice Time - EAS
- Donation and Withdrawal of Electrons
- Regiochemistry in EAS
- Practice Time - Directing Group Effects
- Synthesizing Disubstituted Benzenes: Effects of Substituents on Rate and Orientation
- Steric Considerations
- Strategies for Synthesizing Disubstituted Benzenes
- NAS - Addition/Elimination
- NAS - Elimination/Addition - Benzyne
- Alcohols and Phenols
-
Ethers and Epoxides
- Intro and Occurrence
- Crown Ethers and Cryptands
- Preparation of Ethers
- Reactions of Ethers
- Practice Time - Ethers
- Preparation of Epoxides
- Reactions of Epoxides - Acidic Ring Opening
- Practice Time - Acidic Ring Opening
- Reactions of Epoxides - Nucleophilic Ring Opening
- Practice Time - Nucleophilic Ring opening
- Application - Epoxidation in Reboxetine Synthesis
- Application - Nucleophilic Epoxide Ring Opening in Crixivan Synthesis
- Physical Properties of Ethers and Epoxides
- Naming Ethers and Epoxides
-
Aldehydes and Ketones
- Naming Aldehydes and Ketones
- Physical Properties of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Practice Time - Naming Aldehydes/Ketones
- Nucleophilic addition
- Addition of Water - Gem Diols
- Practice Time - Hydration of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Addition of Alcohols - Hemiacetals and Acetals
- Acetal Protecting Groups
- Hemiacetals in Carbohydrates
- Practice Time - Hemiacetals and Acetals
- Addition of Amines - Imines
- Addition of Amines - Enamines
- Practice Time - Imines and Enamines
- Application - Imatinab Enamine Synthesis
- Addition of CN - Cyanohydrins
- Practice Time - Cyanohydrins
- Application - Isentress Synthesis
- Addition of Ylides - Wittig Reaction
- Practice Time - Wittig Olefination
- Structure of Ketones and Aldehydes
- Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
- Enols and Enolates
- Condensation Reactions
-
4.
NMR, IR, UV and MS
- Spectroscopy
-
HNMR
- Nuclear Spin
- Interpreting
- Chemical Shift
- Practice Time! - Chemical Shift
- Equivalency
- Indentifying Homotopic, Enantiotopic and Diastereotopic Protons
- Practice Time! - Equivalency
- Intensity of Signals
- Spin Spin Splitting
- Practice Time! - Spin-Spin Splitting
- Primer on ¹³C NMR Spectroscopy
- Alkanes
- Alkynes
- Alcohols
- Alkenes
- Coupling in Cis/Trans Alkenes
- Ketones
- HNMR Practice 1
- HNMR Practice 2
- HNMR Practice 3
- HNMR Practice 4
- Exchangeable Protons and Deuterium Exchange
- IR - Infrared Spectroscopy
- UV - Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
- Mass Spectrometry
-
5.
General Chemistry
- General Chemistry Lab
- Strategy for Balancing Chemical Reactions
- Calculator Tips for Chemistry
- Significant Figures
- Practice Time! Significant Figures
- Spreadsheets - Getting Started
- Spreadsheets - Charts and Trend lines
- Standard Deviation
- Standard Deviation Calculations
- Factor Labels
- Practice Time! - Factor Labels
- Limiting Reagent Problem
- Percent Composition
- Molar Mass Calculation
- Average Atomic Mass
- Empirical Formula
- Practice time! Empirical and Molecular Formulae
- Initial Rate Analysis
- Practice Time! Initial Rate Analysis
- Solving Equilibrium Problems with ICE
- Practice Time! Equilibrium ICE Tables
- Le Chatelier's
- Practice Time! Le Chatelier's Principle
- 6. Organic Chemistry Lab
- 7. Tools and Reference
-
8.
Tutorials
- Reaction Mechanisms (introduction)
- Factor Labels
- Acetylides and Synthesis
- Drawing Cyclohexane Chair Structures
- Drawing Lewis Structures
- Aromaticity Tutorial
- Common Named Aromatics (Crossword Puzzle)
- Functional Groups (Flashcards)
- Characteristic Reactions of Functional Groups
- Alkyl and Alkenyl Groups
- Valence Bond Theory
- Alkane Nomenclature
-
9.
The Alchemy of Drug Development
- Ivermectin: From Merck Innovation to Global Health Impact
- The Fen-Phen Fix: A Weight Loss Dream Turned Heartbreak
- The Asymmetry of Harm: Thalidomide and the Power of Molecular Shape
- Semaglutide (Ozempic): From Lizard Spit to a Once-Weekly Wonder
- From Cocaine to Novocain: The Development of Safer Local Anesthesia
- The Crixivan Saga: A Targeted Strike Against HIV
- The story of Merck’s COX-2 inhibitor, Vioxx (rofecoxib)
- The Accidental Aphrodisiac: The Story of Viagra
- THC: A Double-Edged Sword with Potential Neuroprotective Properties?
- Ritonavir Near Disaster and Polymorphism
- 10. Allied Health Chem
Clear History
Quick Menu
Calorimetry
5.2 Calorimetry
Background: The System and the Surroundings
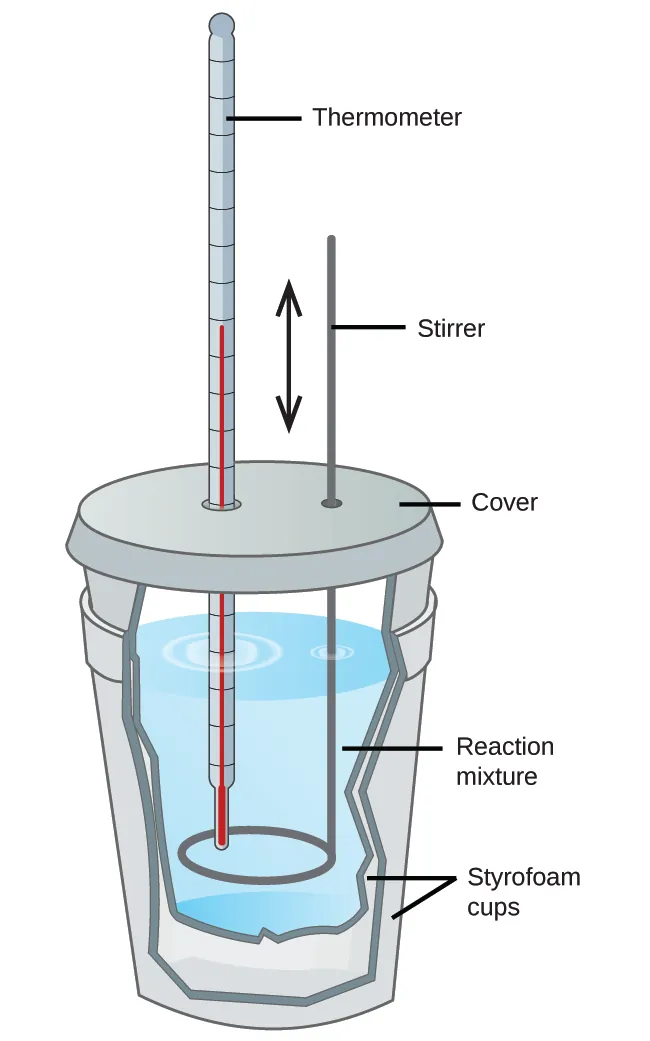
Calorimetry is the technique used to measure the amount of heat transferred to or from a substance during a chemical or physical process. To understand the math, we must define two areas:
- The System: The specific substance(s) undergoing the change (e.g., the chemical reaction).
- The Surroundings: Everything else in contact with the system that serves to provide or absorb heat (e.g., the water in the calorimeter, the cup itself, the thermometer).
A Calorimeter is a device designed to minimize heat exchange with the outside world, effectively trapping the heat so we can measure it. In a "perfect" calorimeter, the heat lost by the system is exactly equal to the heat gained by the surroundings:
qsystem + qsurroundings = 0
(or: qsystem = −qsurroundings)
✏️ Integrated Practice: Heat Transfer Between Substances
A 360.0-g piece of hot steel rebar is dropped into 425 mL of water (425 g) initially at 24.0 °C. The water temperature rises to a final equilibrium of 42.7 °C.
Step 1 (Part A): Calculating Heat Gained by Water
Using the specific heat of water (4.184 J/g°C), calculate how many Joules of heat the water absorbed from the metal.
Hint: qw = cw × mw × (Tfinal - Tinitial, water)
qw = (4.184 J/g°C) × (425 g) × (42.7°C - 24.0°C)
qw = 33,250 J
Step 2 (Part B): Determining the Metal's Initial Temperature
Since qrebar = −qwater, the rebar lost 33,250 J (q = -33,250 J). If the specific heat of steel is 0.449 J/g°C, what was the initial temperature of the rebar?
Question: Rearrange q = c × m × (Tf - Ti) to solve for Ti.
-33,250 J = (0.449 J/g°C) × (360.0 g) × (42.7°C - Ti)
-33,250 / 161.64 = 42.7 - Ti
-205.7 = 42.7 - Ti
Ti = 248.4 °C
Background: Reaction Calorimetry
When we perform a chemical reaction inside a calorimeter, the aqueous solution absorbs or releases the heat of the reaction. For these problems, we often assume the solution has the same density (1.0 g/mL) and specific heat (4.184 J/g°C) as pure water.
✏️ Integrated Practice: Exothermic Neutralization
50.0 mL of HCl and 50.0 mL of NaOH are mixed (Total volume = 100.0 mL). The temperature of this 100.0 g "surroundings" solution rises from 22.0 °C to 28.9 °C.
Step 1 (Part A): Calculating Solution Heat
Calculate the heat gained by the 100.0 g solution (qsoln) using the specific heat of water. Click for Part A Answer
qsoln = (4.184 J/g°C) × (100.0 g) × (28.9°C - 22.0°C)
qsoln = 2,887 J (approx. 2.9 kJ)
Step 2 (Part B): Interpreting the Reaction
Based on your answer in Part A, is the chemical reaction exothermic or endothermic, and what is the value of qrxn? Click for Part B Answer
Since the solution gained heat, the reaction must have released it.
qrxn = −2.9 kJ. This is an Exothermic reaction.
Clinical Application: Hand Warmers
Exothermic reactions are used in medical hand warmers. Some use the crystallization of sodium acetate, while others use the oxidation of iron. In both cases, the chemical system releases heat that your hands (the surroundings) absorb.